Rhenium-SCT
Painless Non-Invasive Skin Cancer Therapy
The Rhenium-SCT® (Skin Cancer Therapy) is a brachytherapy utilizing the Beta emitter radioisotope Rhenium-188 for the treatment Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer.
The Rhenium-SCT® is a medical procedure which is non-invasive. A procedure is considered non-invasive when no break or cut in the skin is created. This means no stitches or the possibility of secondary infection.
The Rhenium-SCT® is a painless therapy with no anaesthesia needed. Especially good for elderly patients, patients with allergies and patients with multiple morbidities or low tolerance to pain.
The Rhenium-SCT® is a single-session treatment in most all cases.
The Rhenium-SCT® is a medical procedure which is non-invasive. A procedure is considered non-invasive when no break or cut in the skin is created. This means no stitches or the possibility of secondary infection.
The Rhenium-SCT® is a precise, personalised therapy that is only applied to the area needed to treat. This means that no unnecessary healthy tissue is damaged either in the depth or outside of the safety border.
Easy and practical thank the simple application and short treatment duration.
Sensational aesthetic results with little or no scarring, considerably fast healing period, no stress treatment, restored functionality.
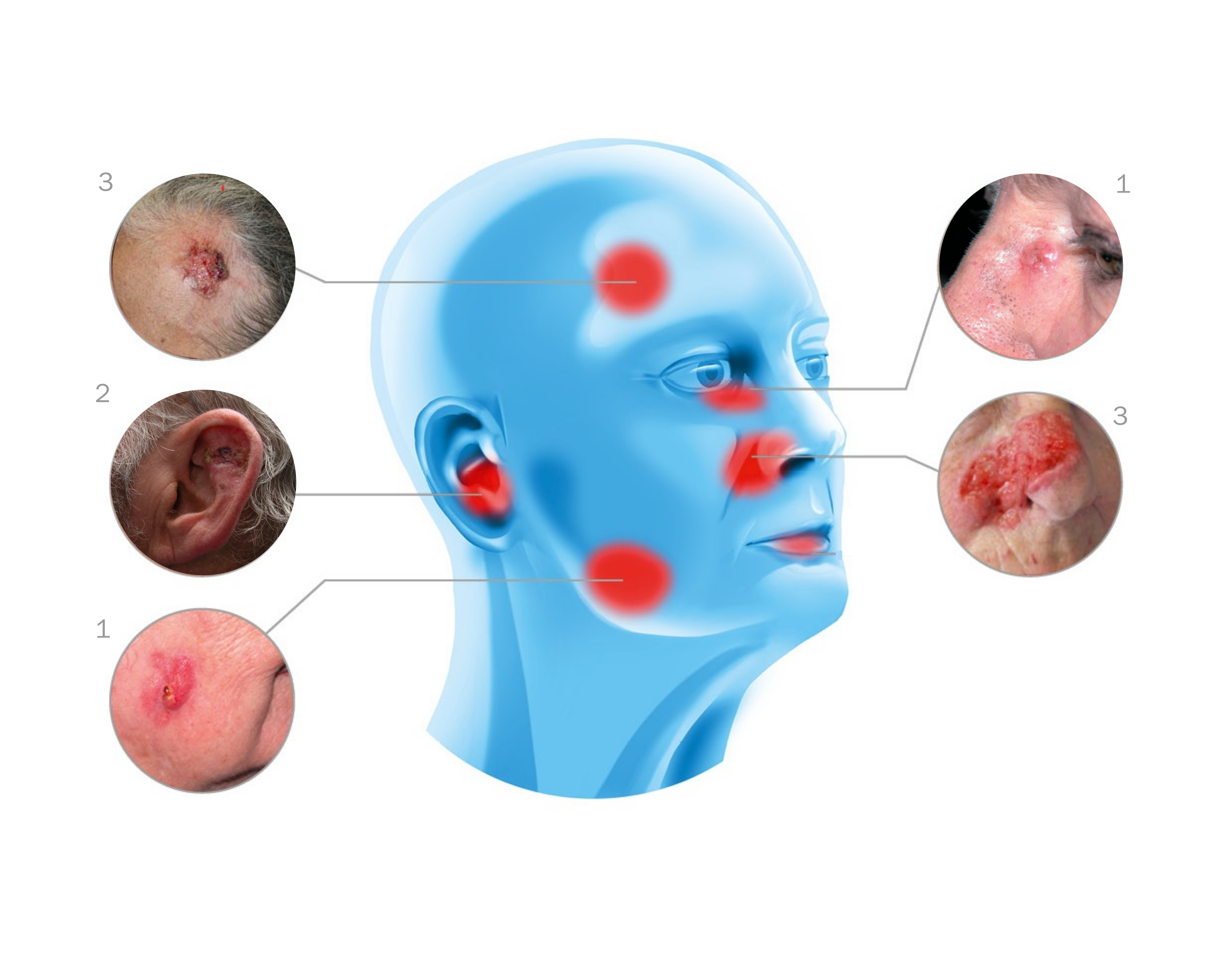
Facts about Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
Over 5 Million
cases every year
1
80% are Basal Cell and 20% are Squamous Cell Carcinomas 2
1 in 5
over 70
have had at least one NMSC diagnosed.3
What is the Rhenium-SCT®?
The Rhenium-SCT® (Skin Cancer Therapy) is a brachytherapy utilizing the Beta emitter radioisotope Rhenium-188 for the treatment of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer.
The main objective of the Rhenium-SCT® is to be a painless, personalized, non-invasive therapy targeting and destroying cancer cells in the area needed to treat.
Medical working principle
This epidermal radioisotope therapy is based on the local direct cell-killing effect of the beta-radiation, which triggers both the local death of cells and local reactions of the immune system of the body to repair itself.
How does the Rhenium-SCT work?
What is Rhenium-188?
Rhenium-188 is an isotope that emits ß-radiation, which has excellent therapeutic advantages.
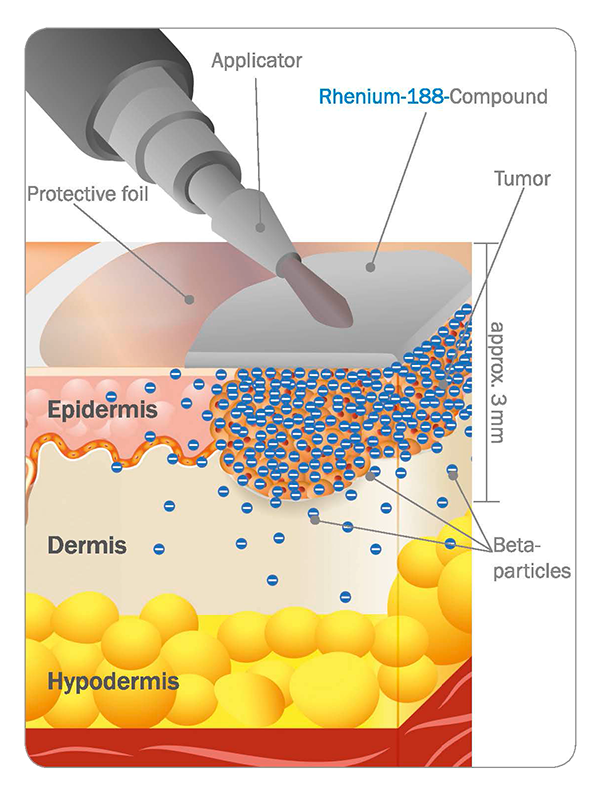
ß-radiation is the emission of ß-particles, which can penetrate the human tissue only up to 2-3 mm deep. Therefore, rhenium-188 is ideal in treating superficial tissue without affecting other parts of the body.
It has a half-life of 17 hours, which means that the radioactivity decays up to the half in 17 hours while emitting ß-radiation. This allows treatments to be performed in a very short period of time.
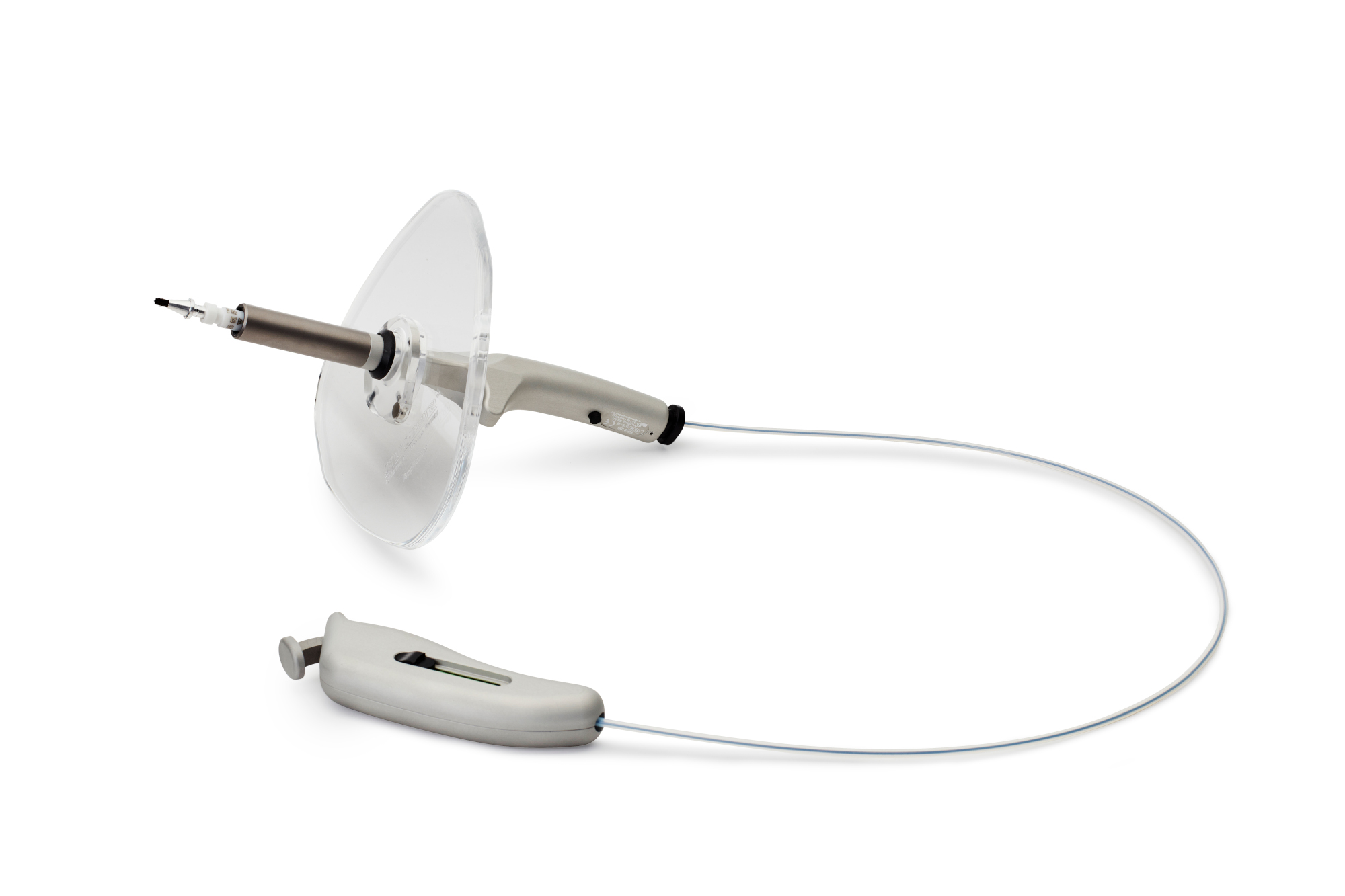
The Oncobeta® Applicator
The Oncobeta® Applicator is a specially designed application device which enables the clinician to apply the Rhenium-SCT® compound in a homogenic manner to the area needed to treat.
The specially designed shielding of the applicator consists of ideal materials for protection which has gone through numerous and extensive testing. The Oncobeta® Applicator is significantly designed to protect both the clinician and patient.
The Rhenium-188 Compound
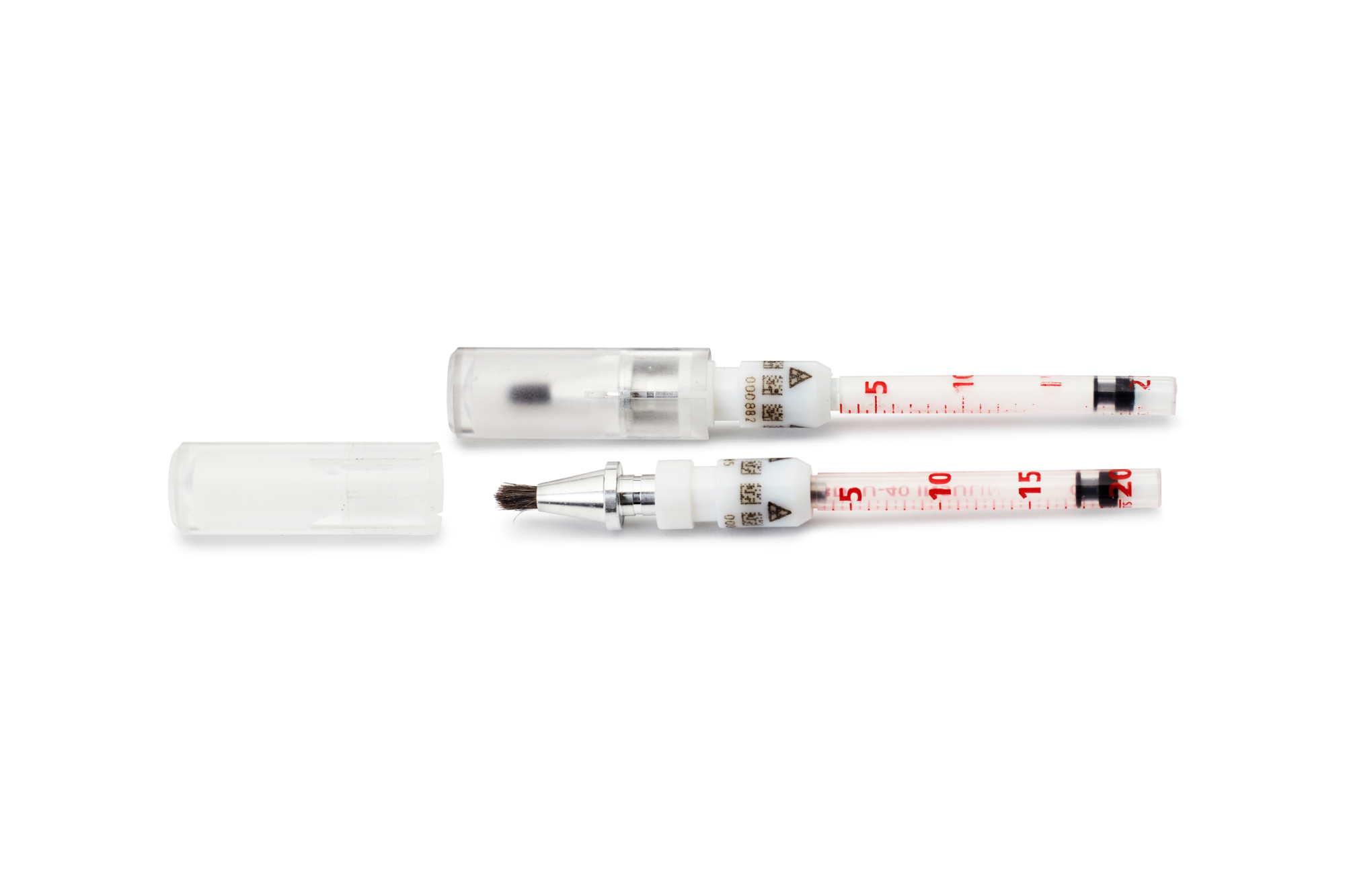
Rhenium-188 is bound to a fluid matrix or “compound” in order to enable an application precisely over the tumour.
The Rhenium-188-Compound is filled in so called carpoules which include a specially designed brush for precise application.
The Carpoules are loaded into the special Oncobeta® applicator for safe handling and efficient usage.
The lesion or the area needed to treat is first covered with a special protective foil.
During the Rhenium-SCT®, the physician is able to apply the exact needed amount of the Rhenium-188-Compound accurately and efficiently utilizing the specifically developed mechanical control. This way the compound is applied homogeneously and precisely over the tumour or area needed to treat.
Steps of the Rhenium-SCT®

MARK
The physician marks the area needed to treat with a dermatological pen.
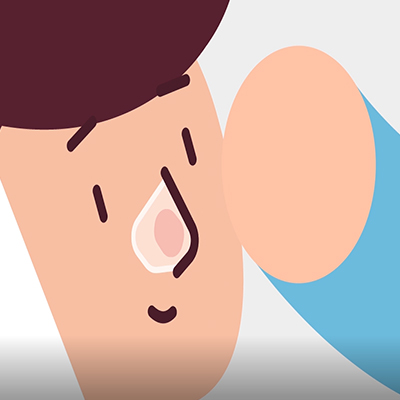

COVER
The area needed to treat is first covered with a special protective foil.
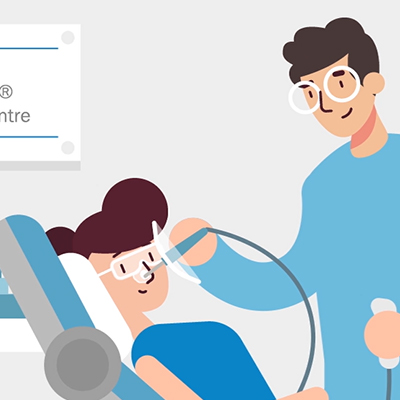

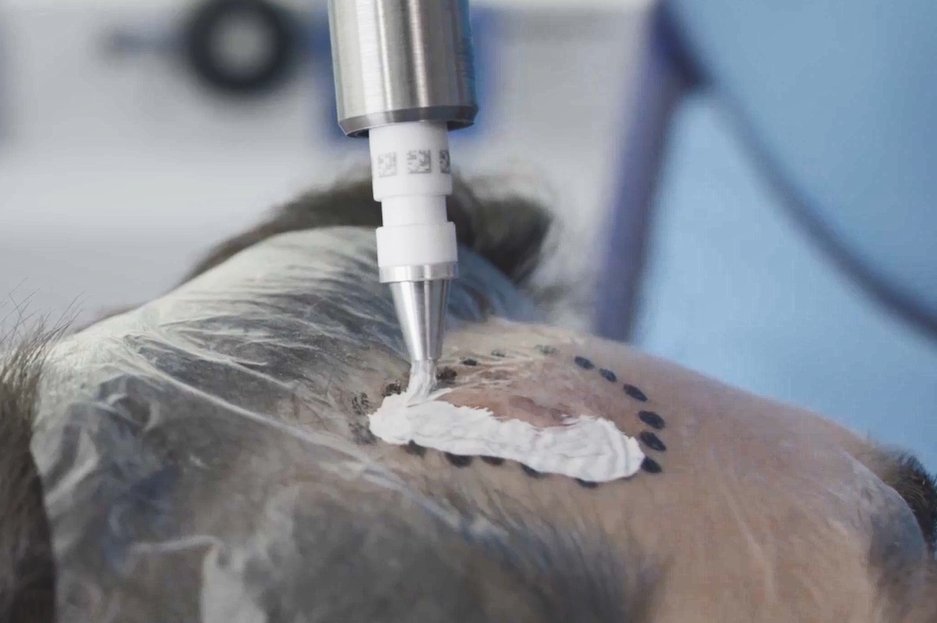
APPLY
The Rhenium-188-Compound is then applied on top of the special foil, over the marked area of treatment with the Oncobeta® Applicator. The foil and compound are to stay in place until the end of the procedure.
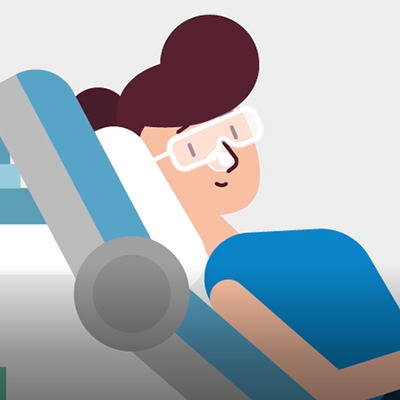

TREATMENT DURATION
The treatment takes approximately 30 to 180 minutes after the compound has been applied. The patient sits or lays comfortably while the Rhenium-188 compound works on the lesion. The protective foil and the dry Rhenium-188-Compound are removed after the designated treatment time.
FOLLOW UP
In general, there is no special aftercare needed. The dead tumour cells are gradually disposed of by the body and replaced with new healthy cells. It is recommended a follow-up with the dermatologist.
Which cases can be treated with Rhenium-SCT®?
The Rhenium-SCT® is approved in Europe, South Africa and Australia for the treatment of basal and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin.
In general, the Rhenium-SCT® can be applied to any location on the body. It can be applied to single and/or multiple lesions of almost any shape or size in just one session. It is also suitable for patients of any age as well as patients with previously treated or complicated lesions.
The Rhenium-SCT® is not recommended for minors or pregnant patients.
Sedda AF, et al. Dermatological high-dose-rate brachytherapy for the treatment of basal and squamous cell carcinoma. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 2008; 33: 745–749.
Cipriani C, et al. Personalized High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy with Non-Sealed Rhenium-188 in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. International Journal of Nuclear Medicine Research, 2017. E-ISSN: 2408-9788/17.
Cipriani, C., and Sedda, A. F.. “Epidermal Radionuclide Therapy – Dermatological High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy for the Treatment of Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinoma.” In Therapeutic Nuclear Medicine, edited by Baum, R. P. New York: Springer, 2014.
Sousa J, et al. Basal Cell Carcinoma on the Vermilion Border of the Lip: A study of six cases. Dermatology. 2001; 209: 131-134.
Before and After Treatment Comparison
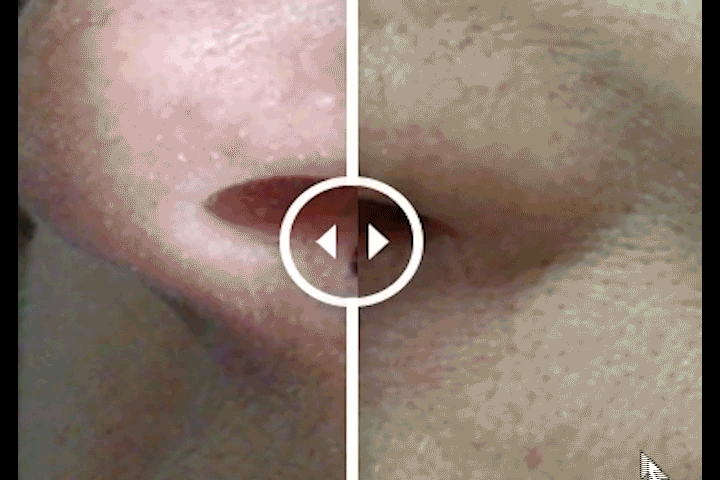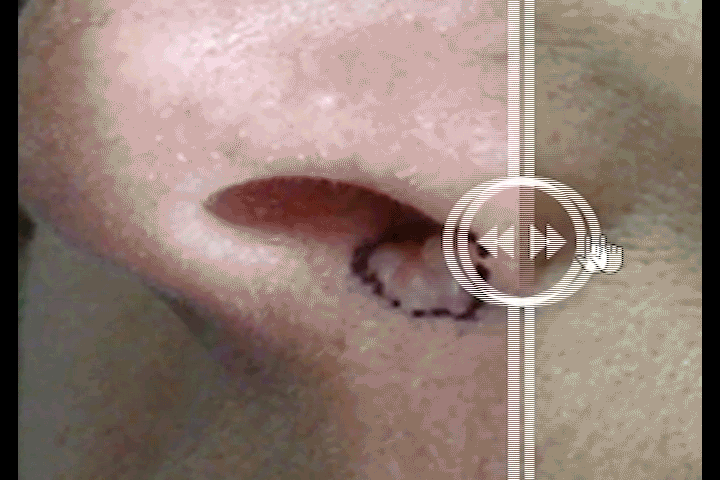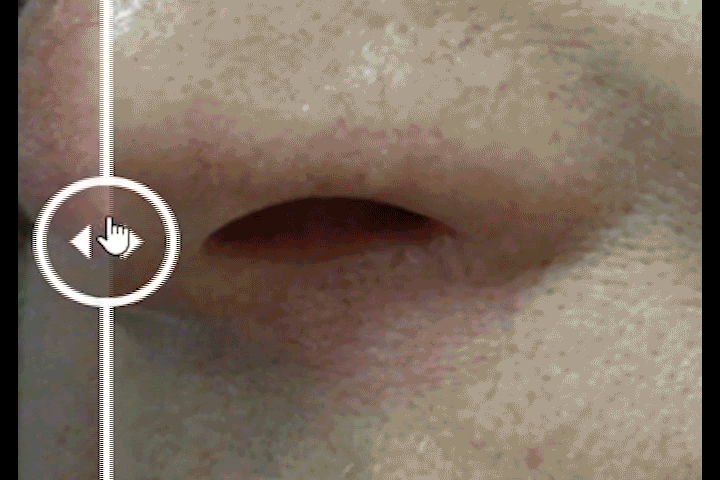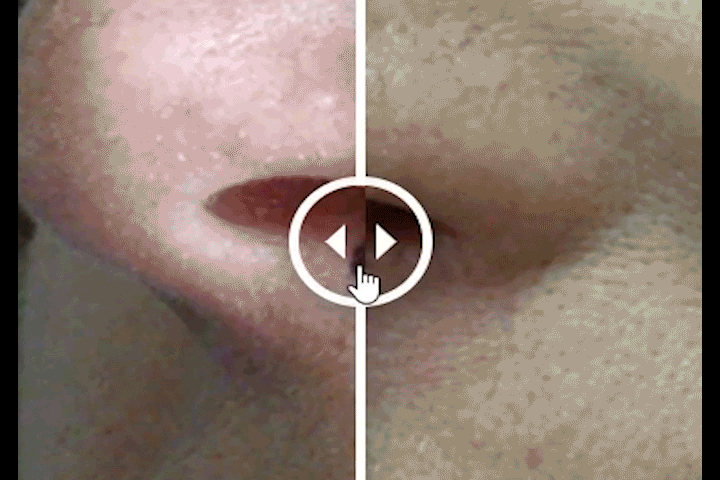
To view before and after images drag the slider.
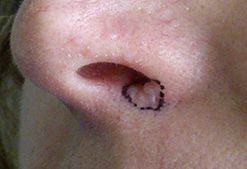
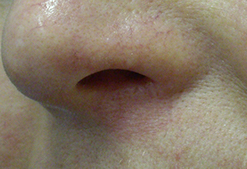
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
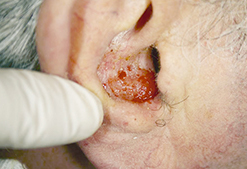
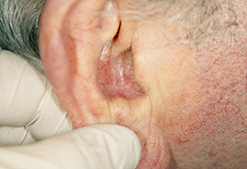
Basal Cell Carcinoma
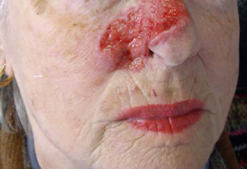
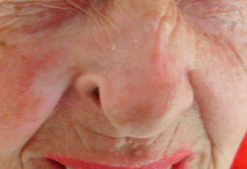
Ulcerated Basal Cell Carcinoma
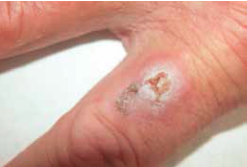
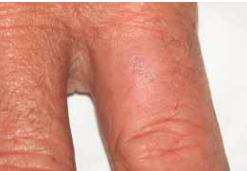
Squamous Cell Carcinoma